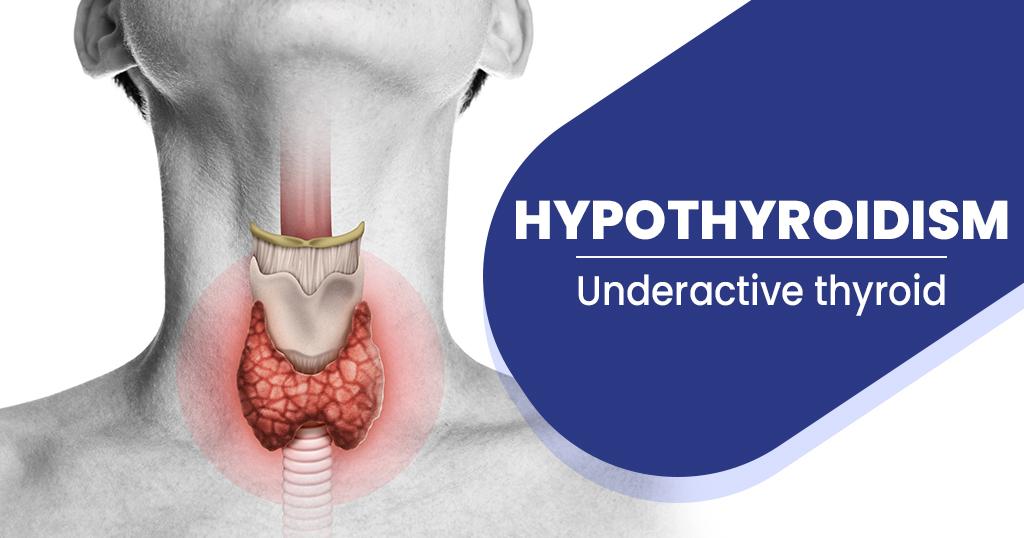
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, is a condition in which the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough thyroid hormones. These hormones are essential for regulating metabolism, and a deficiency can lead to various health issues. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing hypothyroidism effectively.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, hair loss, and constipation. Additionally, individuals may experience depression, muscle weakness, and joint pain. These symptoms can vary in severity and often develop gradually.
Causes
Hypothyroidism can result from various factors, including autoimmune diseases (such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis), radiation therapy, thyroid surgery, certain medications, and iodine deficiency. In some cases, it can be congenital or caused by pituitary gland disorders.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism typically involves blood tests to measure levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4). Elevated TSH and low T4 levels indicate hypothyroidism. In some cases, additional tests may be required to determine the underlying cause.
Treatment
The primary treatment for hypothyroidism is thyroid hormone replacement therapy, usually in the form of synthetic thyroxine (levothyroxine). This medication helps restore normal hormone levels, alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Regular monitoring and dosage adjustments are necessary to ensure effective treatment.